

The first approximation is the simplest of the three. Top to bottom: first, second and third approximations, increasing in accuracy. Although the stated continuous current is 1A, the diode can handle more current if the duration of the pulse is short enough, up to 30A if a single half-sine wave at 60Hz is passed through it. Three diode models are shown in Figure 2.4. It can be used in rectifier and reverse voltage protection applications in electronic appliances like chargers. The Zener Diode will not conduct electricity from the cathode to the anode until the breakdown voltage. The M7 is a high voltage rectifier diode with a high continuous current capacity of 1A. The M7 is a high voltage rectifier diode with a high continuous current capacity of 1A. The cathode is typically connected to a positive voltage.

Note: Complete technical details can be found in the M7 diode datasheet linked at the end of this page. A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance). If you forget which way current flows through a diode, try to remember the mnemonic ACID: 'anode current in diode' (also anode cathode is diode).
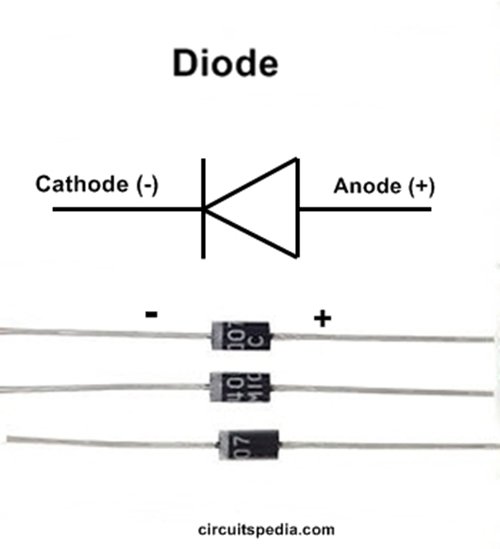
Current can flow from the anode end to the cathode, but not the other direction. It is mainly found in bridge rectifiers in power supplies and other electronic appliances. The positive end of a diode is called the anode, and the negative end is called the cathode. The M7 is a high voltage surface mount diode that is analogous to the popular 1N4007, with a high reverse breakdown voltage of 1kV and a continuous current capacity of 1A.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
